Standardized Snow Water Equivalent (SWE) / Hypsome-SWE
Montana Climate Office
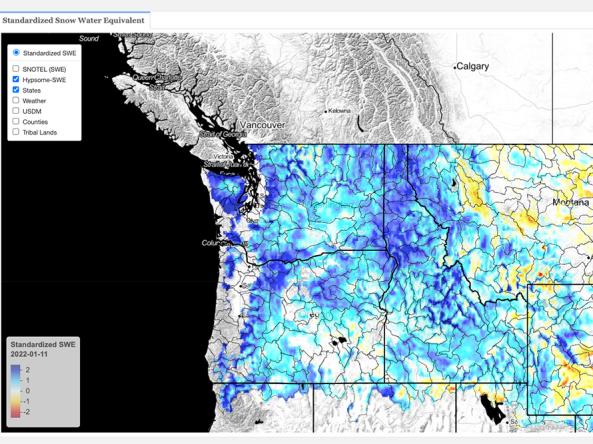
This dataset contains estimates of standardized snow pack anomalies based on the depth of snow water equivalent (SWE), from the NOAA National Weather Service’s National Operational Hydrologic Remote Sensing Center (NOHRSC) SNOw Data Assimilation System (SNODAS). SNODAS is a modeling and data assimilation system developed by NOHRSC to provide the best possible estimates of snow cover and associated parameters to support hydrologic modeling and analysis. Standardization is conducted using a similar framework to computation of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI, gamma probability distribution assumed). Negative (red) values represent below-average SWE while positive (blue) values represent above-average SWE. Standardization is based on data from 2004–present and computed daily.
Hypsome-SWE is a method to evaluate the distribution of SWE across watersheds. Hypsome-SWE is loosely based on the concept of hypsometry, the area-elevation relationship of a basin. However, instead of evaluating the area-elevation relationship, here we evaluate the cumulative SWE (m3)-elevation relationship. More specifically, we compare the median hypsome-SWE curve for a day of interest using the SNODAS period of record (2004–present) to the current day’s SWE distribution. This allows for a rapid assessment of the distribution of SWE within a basin with respect to elevation and allows for an easy comparison to the expected distribution given the SNODAS period of record.
How To
Click on any basin to see the current Hypsome-SWE analysis.