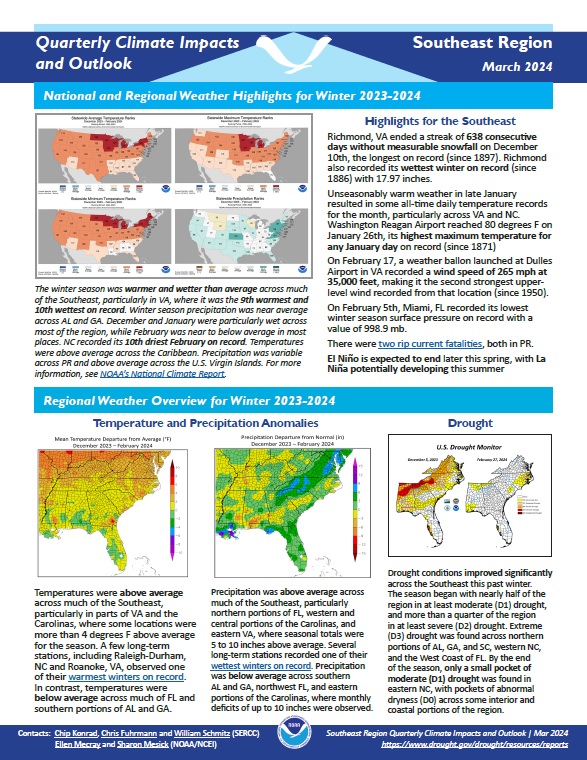
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Southeast and Caribbean Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024. (Updated April 2024 to add Spanish translation of Caribbean information.)
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Gulf of Maine Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024.
Winter was up to 5°C (9°F) warmer than normal, ranking as the warmest on record for a few sites like Caribou, Maine, and Fredericton, N.B., and among the 10 warmest for multiple areas. Precipitation for winter ranged from 50% of normal to more than 200% of normal.
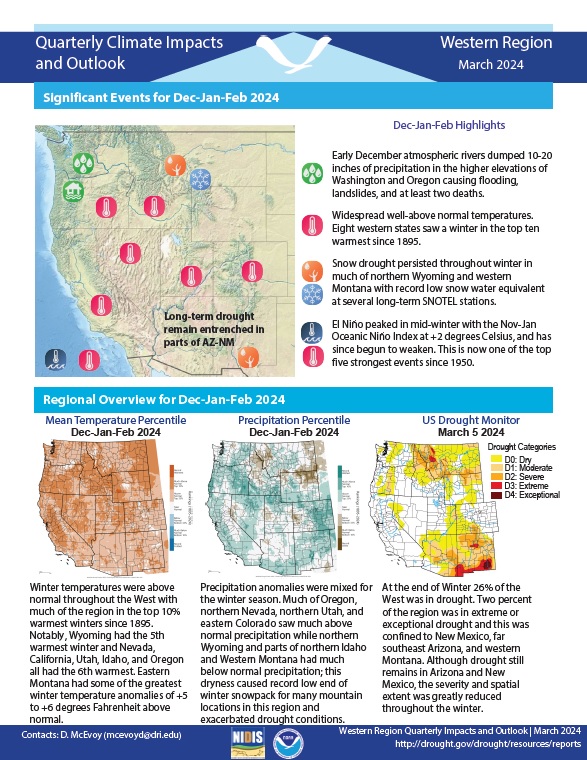
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Western Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024.
Winter temperatures were above normal throughout the West with much of the region in the top 10% warmest winters since 1895. Precipitation anomalies were mixed for the winter season. Much of Oregon, northern Nevada, northern Utah, and eastern Colorado saw much above normal precipitation while northern Wyoming and parts of northern Idaho and Western Montana had much below normal precipitation.
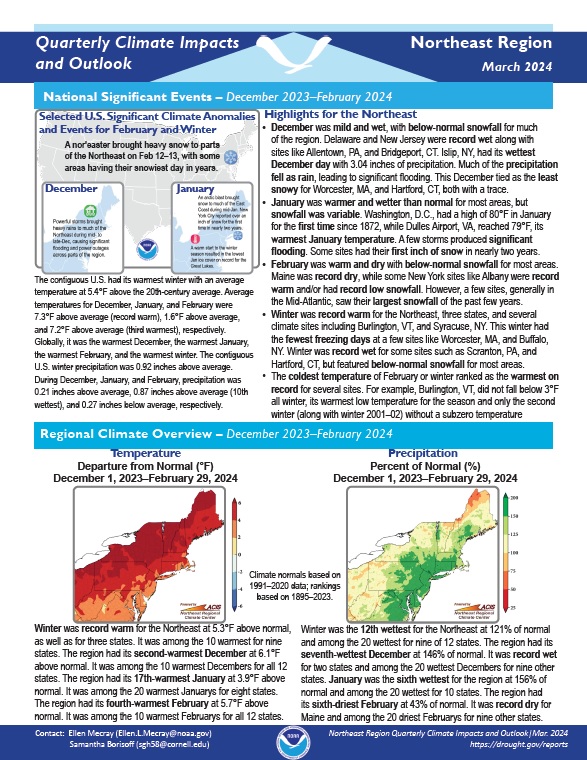
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Northeast Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024.
Winter was record warm for the Northeast at 5.3°F above normal, as well as for three states. It was among the 10 warmest for nine states. Winter was the 12th wettest for the Northeast at 121% of normal and among the 20 wettest for nine of 12 states.
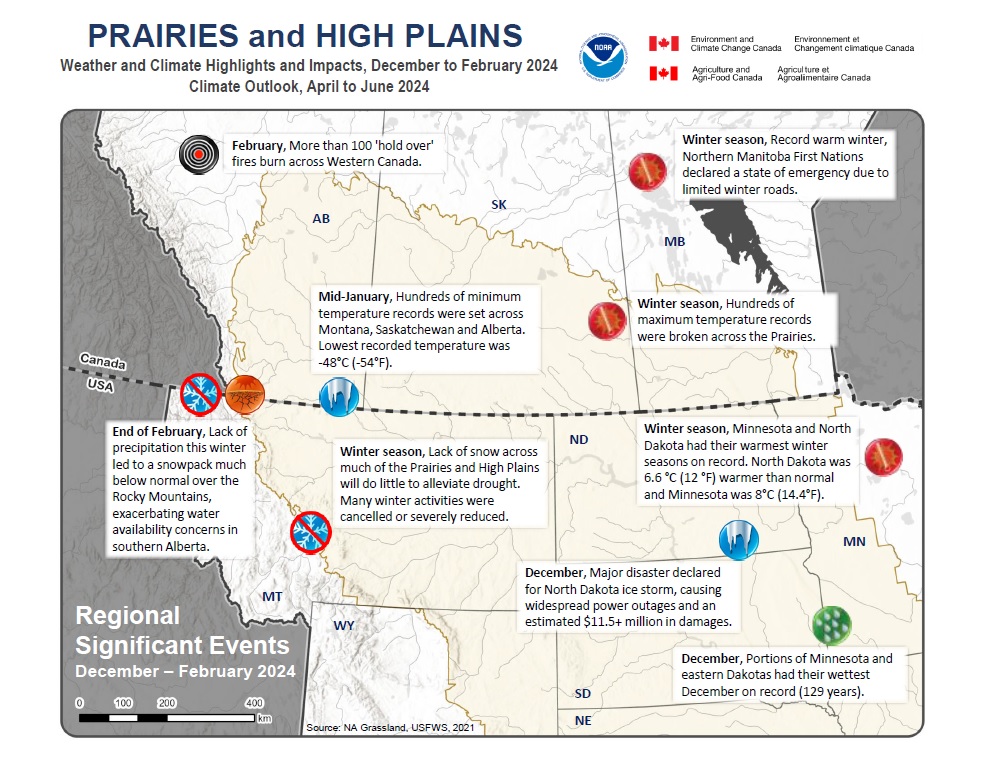
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Canadian and U.S. Prairies and High Plains for December 2023–February 2024, with an outlook for April–June 2024. Dated March 2023.
The Prairies and High Plains saw warmer than normal temperatures, with the eastern half notably warmer than the rest of the region. Much drier than normal conditions were observed across the region in the bordering states and provinces, including inland areas such as the northern Prairies, parts of Montana, Wyoming, and the Dakotas.
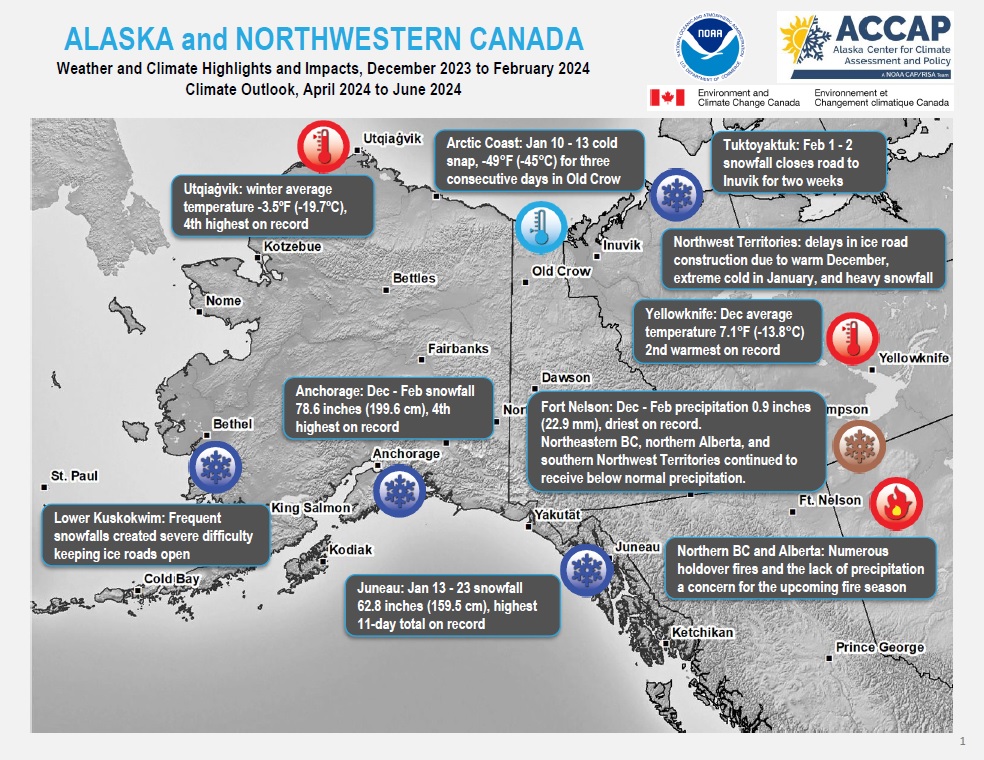
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for Alaska and Northwestern Canada for December 2023–February 2024, with an outlook for April–June 2024. Dated March 2024.
Environment and Climate Change Canada, NOAA, and partners created these climate outlooks to inform the public about recent climate impacts within their respective regions. Each regional report contains easy-to-understand language, and anyone can access them through the U.S. Drought Portal.
Quarterly Climate Impacts and Outlook for the Pacific Region for December 2023–February 2024. Dated March 2024.
For the Dec-Feb (DJF) period, above-normal rainfall was observed across American Samoa, while drier-than-normal conditions prevailed across much of FSM, RMI, Mariana Islands, and the Hawaiian Islands. For the DJF period, moderate to severe drought conditions (D1-D2) were observed in areas of USAPI including Guam, CNMI (Rota, Saipan), FSM (Pingelap, Woleai, Ulithi, Yap Proper), and RMI (Kwajalein, Wotje).
The purpose of the 2023 Pacific Northwest Water Year Impacts Assessment is to summarize the water year conditions and sector impacts as a resource for future management of drought and other climate extremes.
Flash droughts have been recognized within the last few decades as a unique phenomenon with significant impacts that require a different approach to monitoring, prediction, and planning. While there have been efforts to improve flash drought early warning over the last few years, a collaboration amongst researchers and practitioners was needed to ensure a holistic and user-driven approach to improve the country’s understanding and preparedness for flash drought.
An accurate depiction of soil moisture conditions can provide valuable insights for agricultural conditions monitoring, weather prediction, and drought and flood early warning. NOAA’s National Integrated Drought Information System (NIDIS), working in collaboration with the U.S.