For the latest forecasts and critical weather information, visit weather.gov.
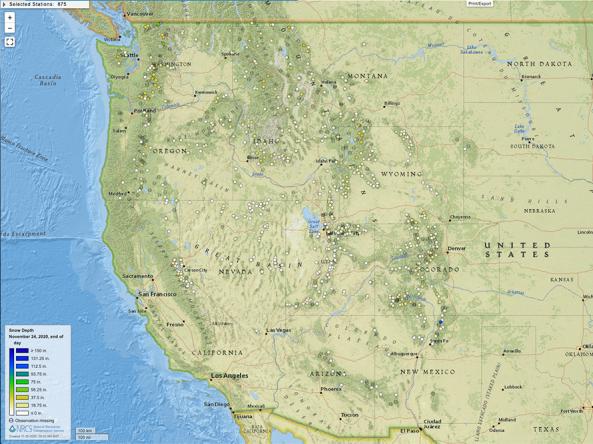
Snow Telemetry (SNOTEL) Snow Depth and Snow Water Equivalent Products
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
As part of the Snow Survey and Water Supply Forecasting Program, the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service's (NRCS) National Water and Climate Center administers an automated snow monitoring program consisting of several types of automated and semi-automated data collection methods.
The National Water and Climate Center provides reports, graphs, and interactive maps based on data from SNOwpack TELemetry Network (SNOTEL) stations. This includes snow depth, snow water equivalent (SWE, the amount of liquid water contained in the snowpack), precipitation, temperature, soil moisture, reservoir, and streamflow data.
About the Snow Telemetry (SNOTEL) Network
The SNOTEL network is composed of over 800 automated data collection sites located in remote, high-elevation mountain watersheds in the western U.S. They are used to monitor snowpack, precipitation, temperature, and other climatic conditions. The data collected at SNOTEL sites are transmitted to a central database, called the Water and Climate Information System, where they are used for water supply forecasting, maps, and reports.
SNOTEL sites are designed to operate unattended and without maintenance for a year or more. A typical SNOTEL remote site consists of measuring devices and sensors, an equipment shelter for the radio telemetry equipment, and an antenna that also supports the solar panels used to keep batteries charged.
A standard sensor configuration includes a snow pillow, a storage precipitation gage, and a temperature sensor. The snow pillow measures how much water is in the snowpack by weighing the snow. Devices in the shelter convert the weight of the snow into the snow's water equivalent (or SWE).
SNOTEL stations also collect data on snow depth, all-season precipitation accumulation, and air temperature with daily maximums, minimums, and averages. Many enhanced SNOTEL sites are equipped to take soil moisture and soil temperature measurements at various depths, as well as solar radiation, wind speed, and relative humidity. The configuration at each site is tailored to the physical conditions, the climate, and the specific requirements of the data users.
This map shows snow water equivalent (SWE)—the amount of liquid water in the snowpack—compared to past conditions. SWE is shown as a percentage of the 1991–2020 median for HUC6 watersheds across the western U.S., based on measurements from Snow Telemetry (SNOTEL) stations. Yellow to red hues indicate below-normal SWE, while blue hues indicate above-normal SWE.
View an interactive version of this map for the latest information from the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service.
Percent of Median Snow Water Equivalent
< 50% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is less than 50% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
50%–70% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is between 50%–70% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
70%–90% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is between 70%–90% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
90%–110% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is between 90%–110% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
110%–130% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is between 110%–130% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
130%–150% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is between 130%–150% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
>150% of Median
Current snow water equivalent (SWE) is greater than 150% of the median SWE value for this day of the year, compared to historical conditions from 1991–2020.
This map shows snow water equivalent (SWE)—the amount of liquid water in the snowpack—compared to past conditions. SWE is shown as a percentage of the 1991–2020 median for HUC6 watersheds across the western U.S., based on measurements from Snow Telemetry (SNOTEL) stations. Yellow to red hues indicate below-normal SWE, while blue hues indicate above-normal SWE.
View an interactive version of this map for the latest information from the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service.
This map is updated daily, with a 2-day delay. The snow water equivalent (SWE) values shown on the map reflect conditions 2 days ago (the date shown below the map) based on data provided by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) yesterday. NRCS may make additional adjustments to these data. For the most up-to-date information, view NRCS's interactive map.
How to
View the National Water and Climate Center's Snow and Water Products Guide to view a directory of products and user guides.
Download Data
Download Data from the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS):
- SOAP Web Service: Access to machine-readable data from the Air & Water Database using a SOAP protocol. View the user guide.
- RESTful API Web Service: Access to machine-readable data from the Air & Water Database using a REST protocol.