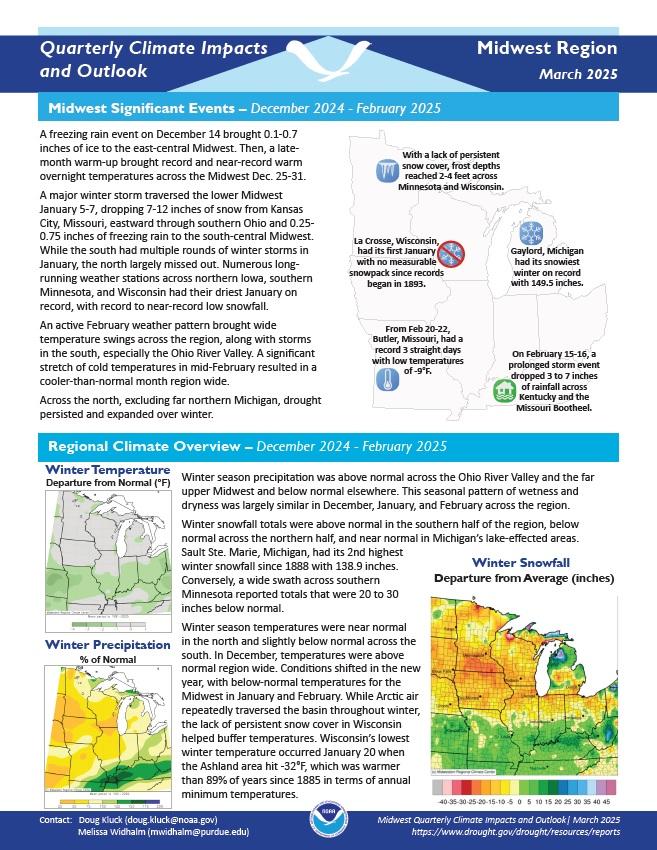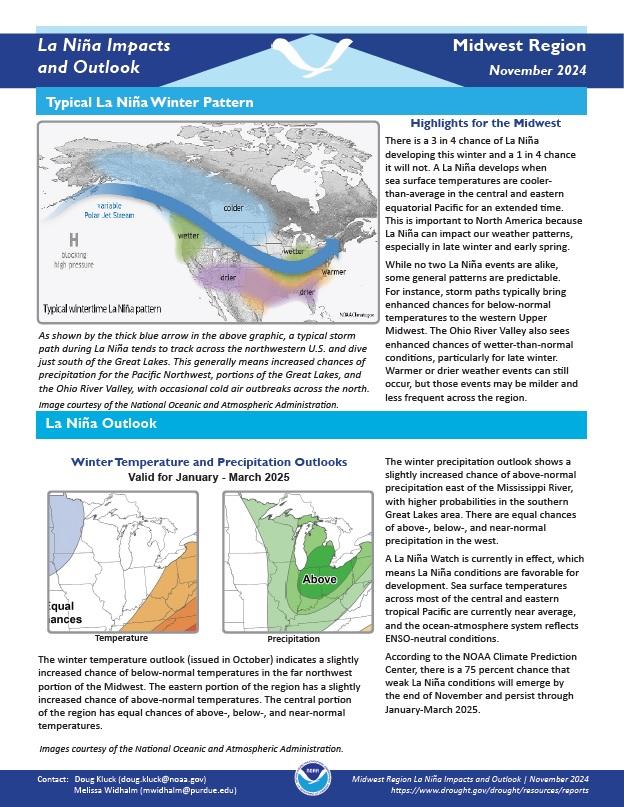
Midwest
Precipitation extremes in the Midwest have a major impact on the region’s resources, economic sectors, and residents. Over the last century, precipitation trends in the Midwest have been moving towards wetter conditions and fewer droughts than the region experienced in the early 20th century. However, the Midwest has still felt adverse impacts during recent droughts, particularly in 1988 and 2012. These adverse impacts include limited barge transportation on major rivers (including the Mississippi River), decreased agricultural production, challenges for municipal water supply and quality, and reduced productivity for hydropower. An added challenge in recent years has been the tendency to transition from drought to flood and back to drought within short time spans, sometimes within a matter of months. NIDIS and its partners launched the Midwest DEWS in response to the 2012 drought, which highlighted the need for additional drought early warning and preparedness in the region.
Primary contact: Molly Woloszyn, Regional Drought Information Coordinator
Featured Activity
Midwest DEWS Partners Meeting: Presentations Now Available
NIDIS held the Midwest Drought Early Warning System (DEWS) Partners Meeting on August 20–22, 2024 in Indianapolis, Indiana. This regional gathering provided the opportunity for partners in the Midwest DEWS to share and discuss ongoing drought-related activities, learn about new and innovative drought research and resources, explore emerging issues and opportunities, and identify collaborative paths forward to advance drought early warning and preparedness in the region. Presentations from the meeting are available.
Regional Activities
The following table highlights activities in the Midwest that are ongoing efforts related to drought, involve multiple partners, serve as a unique way to address regional drought needs, and are related to at least one of the components of drought early warning. Please contact Molly Woloszyn (molly.woloszyn@noaa.gov) for more information about the table or to inquire about getting an activity added to the list.
DEWS Component Legend
The 2022 Midwest and Missouri River Basin DEWS Partners Meeting, which was held on October 13–14, 2022 in Omaha, NE, brought together partners from both the Midwest and…
2022
2022
NIDIS held the Midwest Drought Early Warning System (DEWS)…
2024
2024
This was a pilot project under the U.S. Forest Service’s recently formed Soil Moisture Monitoring Network Initiative. It aimed to explore best practices for forest soil moisture monitoring and…
2021
2023
To improve access and usability of drought and water information across the Mississippi River Basin, NOAA, in partnership with the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, is developing a…
2024
2025
In September 2022, NOAA partnered with the Cooperative Institute for Research to Operations in Hydrology (CIROH), through the University of Minnesota, to develop a pilot project focused on…
Observation + Monitoring
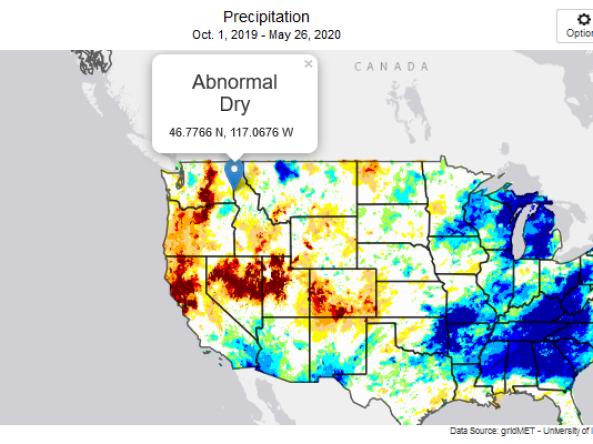
When monitoring drought, it is important to look at data across the spectrum—from the atmosphere, land surface, and water availability below the surface. The list of data and maps below has been customized for the Midwest, and provides a snapshot of conditions across that spectrum, including precipitation and temperature departure data, evaporative demand, streamflow, soil moisture, groundwater, and various derived indices for monitoring drought in the region. Monitoring for the impact of drought is also important, and resources to submit conditions and/or impacts and view conditions are provided.
Regional Data and Maps
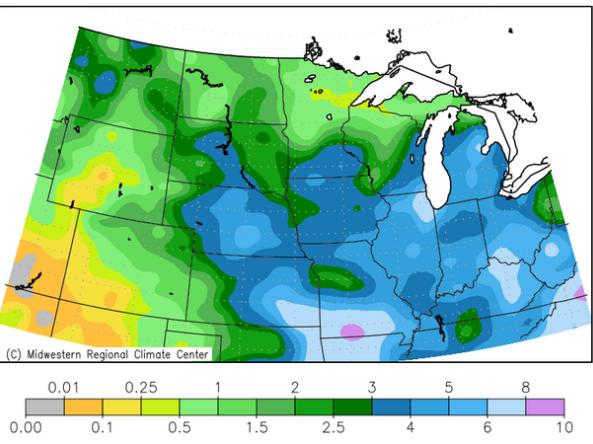
The Midwest Climate Watch is a resource for current climate information for the Midwestern region of the United States, produced by the Midwestern Regional Climate Center (MRCC).
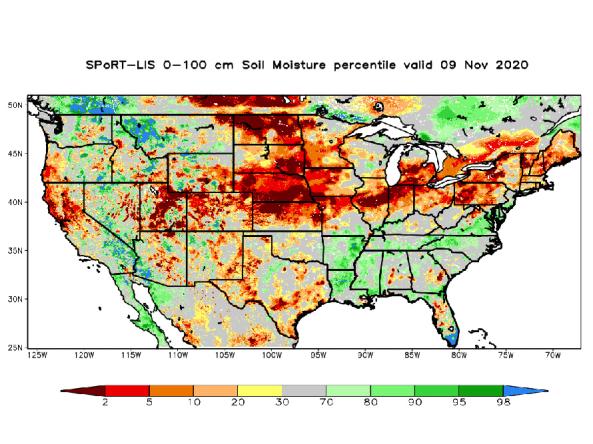
NASA’s Short-term Prediction and Transition Center – Land Information System (SPoRT-LIS) provides high-resolution (about 3-km) gridded soil moisture products in real-time to support regional and lo
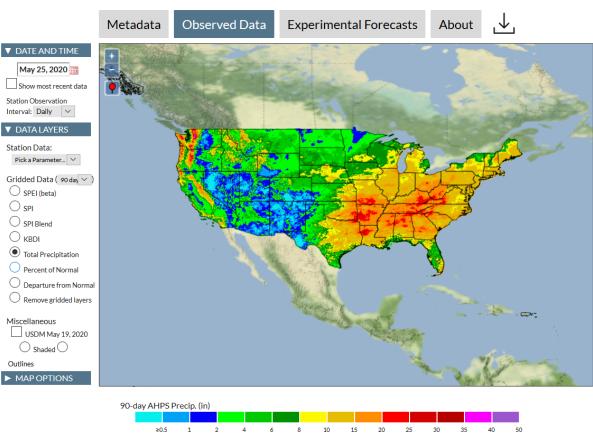
The Integrated Water Portal is a map-driven data exploration and visualization tool that brings together water data from several agencies and allows users to quickly explore regional and local wate
This tool, available as part of The Climate Toolbox, provides maps and summary tables of different drought types, such as agricultural and meteorological drought, for a location in the contiguous U
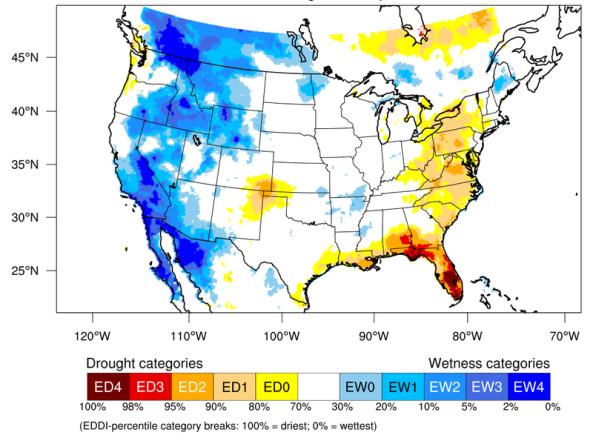
The Evaporative Demand Drought Index (EDDI) is an experimental tool that examines how anomalous the atmospheric evaporative demand (E0; also known as "the thirst of the atmosphere") is for a given
The National Drought Mitigation Center's Drought Impacts Toolkit features several key tools for monitoring and mitigating the impacts of drought, including condition monitoring observer reports, th
Planning + Preparedness
There is little that can be done to influence the weather patterns that cause drought, but preparatory actions and policies can help communities cope with drought impacts. Drought planning can ensure continuity of public services and quality of life. Drought planning can be done at the local and/or state level, or integrated into existing plans (e.g., hazard mitigation planning, land-use planning).
The Midwest DEWS partnered with the National Drought Mitigation Center to analyze drought mitigation and response actions in state and county plans across the region. This database of drought mitigation and response actions can be shared by request. Please reach out to Molly Woloszyn for more information.
Regional Drought Planning Resources
Prediction + Forecasting
When will drought affect me? How long could it last? This section includes resources for drought prediction and forecasting on what could be ahead, including the short-term (e.g., 8–14 day forecast), seasonal to subseasonal (e.g., monthly), and future climate projections (e.g., mid-century). The appropriate time scale will depend upon how this information is being used (e.g., drought response, mitigation management action, long-term planning). Weather and climate prediction is an evolving science, as researchers continue to find ways to improve models and forecasting capabilities at various time scales.
Regional Forecasts and Outlooks
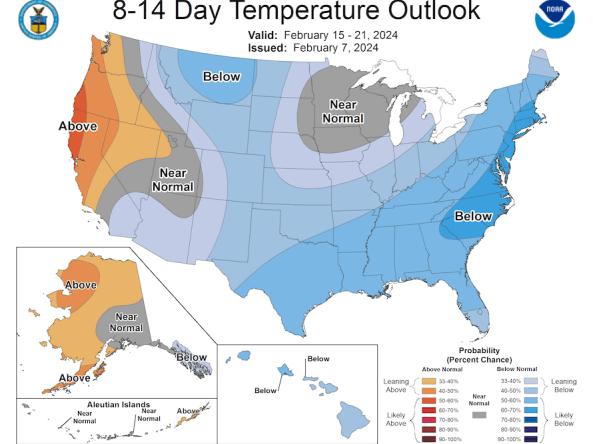
The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) produces temperature and precipitation outlooks for the U.S., including 6-10 day, 8-14 day, monthly, and seasonal outlooks.
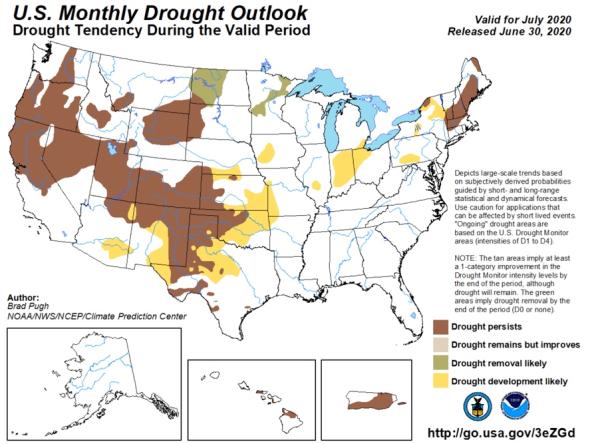
The monthly and seasonal (3-month) outlook for drought tendency from the Climate Prediction Center (CPC), which depicts large-scale trends based on subjectively derived probabilities guided by shor
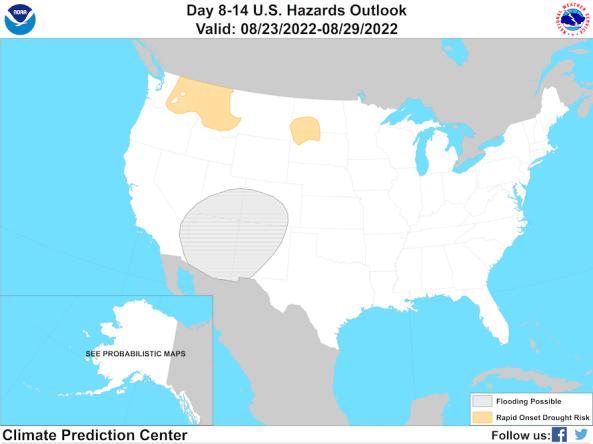
The Climate Prediction Center's Day 8–14 (Week 2) U.S. Hazards Outlook shows potential hazardous conditions related to temperature, precipitation, wind, snow, and rapid onset drought.
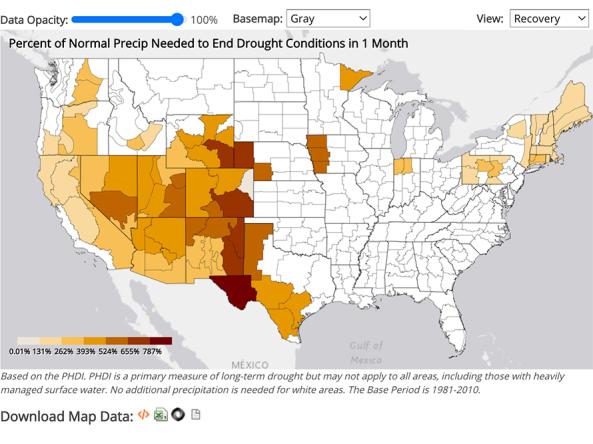
NCEI provides precipitation data that can be used to show probability or the amount of precipitation to ameliorate or end a drought at different monthly scales.
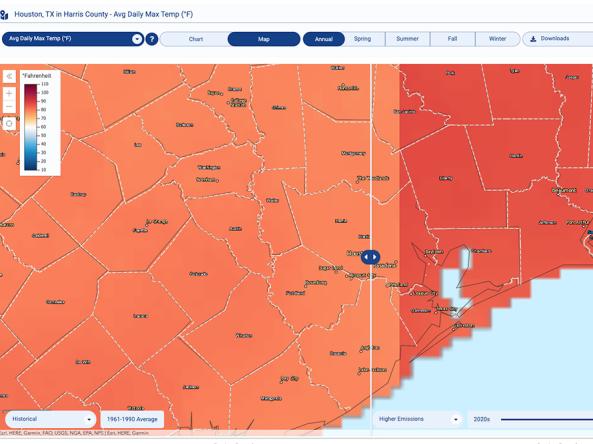
The Climate Explorer offers graphs and maps of observed and projected temperature, precipitation, and related climate variables for every county in the contiguous United States, helping people asse
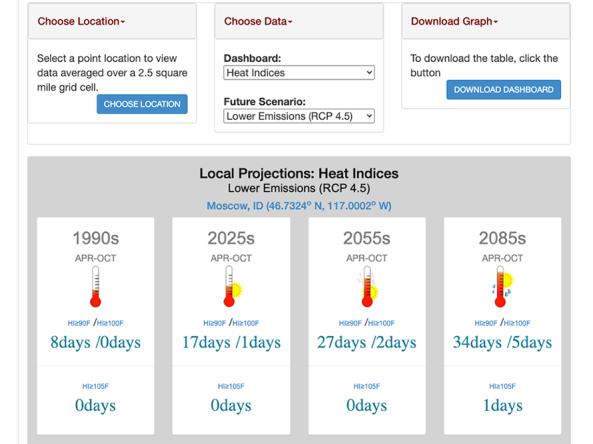
This tool, available as part of The Climate Toolbox, provides a table of future climate projections from an average of 20 global climate models under either high or low future greenhouse gas emissi
Communication + Outreach
An important component for drought early warning is communicating this information to stakeholders across the Midwest region that need this information in order to make more informed decisions. There are various ways drought information is communicated across the Midwest, including a monthly webinar series, a quarterly climate report, and the Midwest DEWS email list.
Regional Communications Documents
Research + Applications
Research to better understand drought in the Midwest and its development, persistence, improvement, and interaction with other hazards is critical to providing timely and reliable information, products, and services in support of drought early warning. This page highlights research projects that are studying drought in the Midwest region, with support from NIDIS.